Difference between revisions of "Orange Pi 5"
(→How to burn Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to TF card) |
(→How to burn Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to TF card) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
[[Image:Pi-5-details-pic14.png]]<br><br> | [[Image:Pi-5-details-pic14.png]]<br><br> | ||
9) Then start to write the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to the TF card<br> | 9) Then start to write the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to the TF card<br> | ||
| − | a. First check '''"SD Boot"''' in '''"Choose function mode'''<br> | + | a. First check '''"SD Boot"''' in '''"Choose function mode"'''<br> |
b. Then select the path of the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image in the '''"Choose firmware"''' column<br> | b. Then select the path of the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image in the '''"Choose firmware"''' column<br> | ||
c. Finally, click the '''"Create"''' button to start burning the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to the TF card<br><br> | c. Finally, click the '''"Create"''' button to start burning the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to the TF card<br><br> | ||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
[[Image:Pi-5-details-pic23.png]]<br><br> | [[Image:Pi-5-details-pic23.png]]<br><br> | ||
[[Image:Pi-5-details-pic24.png]]<br><br> | [[Image:Pi-5-details-pic24.png]]<br><br> | ||
| − | 6) Then turn on the switch of the power adapter. If everything is normal, you can see the startup screen of the system on the HDMI monitor or LCD screen.<br> | + | 6) Then turn on the switch of the power adapter. If everything is normal, you can see the startup screen of the system on the HDMI monitor or LCD screen.<br><br> |
7) If you want to view the output information of the system through the debugging serial port, please use the serial cable to connect the development board to the computer. For the connection method of the serial port, please refer to the section on how to use the debugging serial port in <span style="color:#0066CC;">[http://www.orangepi.org/html/hardWare/computerAndMicrocontrollers/service-and-support/Orange-pi-5.html the Orange Pi 5 user manual:]</span><br><br> | 7) If you want to view the output information of the system through the debugging serial port, please use the serial cable to connect the development board to the computer. For the connection method of the serial port, please refer to the section on how to use the debugging serial port in <span style="color:#0066CC;">[http://www.orangepi.org/html/hardWare/computerAndMicrocontrollers/service-and-support/Orange-pi-5.html the Orange Pi 5 user manual:]</span><br><br> | ||
=== Linux system instructions === | === Linux system instructions === | ||
| − | Ubuntu images and Debian images are generally referred to as Linux images (they both use the Linux kernel), so when you see a Linux image or Linux system in the manual, it refers to a image or system like Ubuntu or Debian.<br> | + | Ubuntu images and Debian images are generally referred to as Linux images (they both use the Linux kernel), so when you see a Linux image or Linux system in the manual, it refers to a image or system like Ubuntu or Debian.<br><br> |
| − | Many people will have doubts about whether they can use pure Ubuntu or pure Debian systems (pure here can be understood as systems downloaded from Ubuntu or Debian official websites). The answer is no, because Ubuntu and Debian do not provide an adapted system for the Orange Pi development board.<br> | + | Many people will have doubts about whether they can use pure Ubuntu or pure Debian systems (pure here can be understood as systems downloaded from Ubuntu or Debian official websites). The answer is no, because Ubuntu and Debian do not provide an adapted system for the Orange Pi development board.<br><br> |
| − | We can see from the official websites of Ubuntu and Debian that they both support the arm64 architecture (the SOC of the development board is the arm64 architecture), but please note that the support mentioned here refers only to the arm64 version of the software warehouse provided by Ubuntu or Debian (including Tens of thousands of software packages) or rootfs (these are the packages that Orange Pi uses when making Ubuntu or Debian systems). To make an Ubuntu or Debian system that can be used for a certain development board also needs to transplant U-boot and Linux kernel, etc., as well as repair the encountered bugs and optimize some functions, all of which are done by Orange Pi.<br> | + | We can see from the official websites of Ubuntu and Debian that they both support the arm64 architecture (the SOC of the development board is the arm64 architecture), but please note that the support mentioned here refers only to the arm64 version of the software warehouse provided by Ubuntu or Debian (including Tens of thousands of software packages) or rootfs (these are the packages that Orange Pi uses when making Ubuntu or Debian systems). To make an Ubuntu or Debian system that can be used for a certain development board also needs to transplant U-boot and Linux kernel, etc., as well as repair the encountered bugs and optimize some functions, all of which are done by Orange Pi.<br><br> |
| − | If Linux distributions such as CentOS, Kali, or OpenWRT are not ported by other developers or ported and adapted by themselves, they cannot be used on the development board of Orange Pi (hardware running these systems is no problem).<br> | + | If Linux distributions such as CentOS, Kali, or OpenWRT are not ported by other developers or ported and adapted by themselves, they cannot be used on the development board of Orange Pi (hardware running these systems is no problem).<br><br> |
In addition, people often ask whether the system of other development boards can be used on the Orange Pi development board. The answer is no, because the chips and circuit connections used by different development boards are generally different. A system developed for a certain development board basically cannot be used on other development boards.<br><br> | In addition, people often ask whether the system of other development boards can be used on the Orange Pi development board. The answer is no, because the chips and circuit connections used by different development boards are generally different. A system developed for a certain development board basically cannot be used on other development boards.<br><br> | ||
1)<span style="color:#0066CC;">[[Supported Linux image types and kernel versions | Supported Linux image types and kernel versions]]</span><br> | 1)<span style="color:#0066CC;">[[Supported Linux image types and kernel versions | Supported Linux image types and kernel versions]]</span><br> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:32, 25 April 2023
Contents
- 1 Getting Started
- 2 What is Orange Pi 5
- 3 Purpose of Orange Pi 5
- 4 Close look of Orange Pi 5
- 5 Starting Orange Pi 5 for the first time
- 5.1 What you need
- 5.2 Download the image of the development board and related materials
- 5.3 Method of burning Linux image to TF card based on Windows PC
- 5.4 How to burn Android image to TF card
- 5.5 How to burn Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to TF card
- 5.6 Start Orange Pi 5
- 5.7 Linux system instructions
- 5.8 Instructions for the use of the Android 12 system
- 6 Parameter table
Getting Started
This guide is designed for Orange Pi 5. The purpose is to learn about Orange Pi 5 as well as how to prepare and set up for basic use.
What is Orange Pi 5
Orange Pi 5 adopts Rockchip RK3588S new-generation octa-core 64-bit ARM processor, specifically quad-core A76 and quad-core A55, using Samsung 8nm LP process technology, large-core main frequency up to 2.4GHz, integrated ARM Mali
-G610 MP4 GPU, embedded with high-performance 3D and 2D image acceleration modules, built-in AI accelerator NPU with a computing power of up to 6 Tops, has 4GB/8GB/16GB/32GB (LPDDR4/4x) memory, and has up to 8K display processing capabilities.
Orange Pi 5 brings out quite a lot of interfaces, including HDMI output, Type-C, M.2 PCIe2.0x1, Gigabit Ethernet port, USB2.0, USB3.0 interface and 26pin expansion pin header, etc. It can be widely used in high-end tablet, edge computing, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, AR/VR, smart security, smart home and other fields, covering various AIoT industries.
Orange Pi 5 supports Orange Pi OS, the official operating system developed by Orange Pi. At the same time, it supports Android 12.1, Debian11, Ubuntu20.04 and Ubuntu22.04 and other operating systems.
Purpose of Orange Pi 5
We can use it to achieve:
- A Linux desktop computer
- A Linux web server
- Android tablet
- Android game console, etc.
Of course, there are more functions, because the Orange Pi 5 development board can install Linux systems such as Debian and Ubuntu, and systems such as Android, which means that we can implement it within the scope of the development board hardware and software support. Various functions.
Close look of Orange Pi 5
Top view:
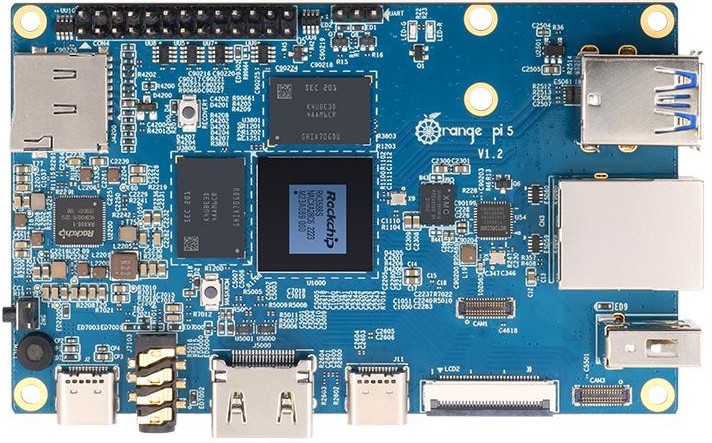
Bottom view:
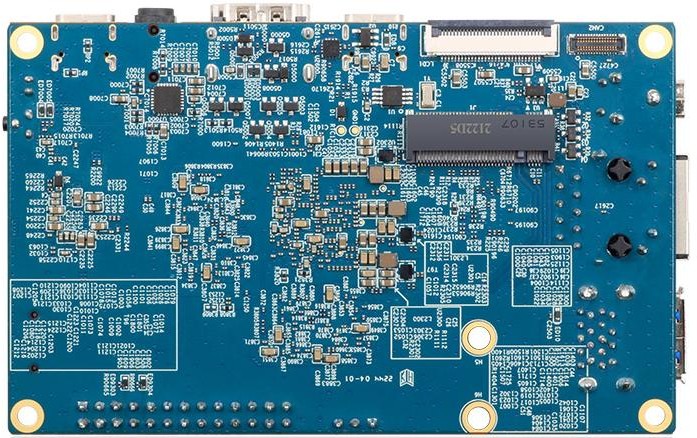
For detailed hardware descriptions and pinouts, please refer to the Orange Pi 5 detail page。
Starting Orange Pi 5 for the first time
Orange Pi 5 can be started in two ways, one is to burn the image to the SSD and the other is to burn the image to the TF card.
What you need
- Orange Pi 5 main board
- TF card, a class 10 or above high-speed SanDisk card with a minimum capacity of 8GB (32GB or above is recommended)
- TF card reader, used to burn the image into the TF card
- Display with HDMI interface
- HDMI to HDMI cable, used to connect the development board to an HDMI monitor or TV for display
- Type-C to HDMI cable, connect the development board to an HDMI monitor or TV for display through the Type-C interface
- Type-C to USB adapter, used to connect USB storage devices or USB devices such as mouse and keyboard
- 10.1-inch MIPI screen, used to display the system interface of the development board
- Power adapter, Orange Pi 5 is recommended to use 5V/4A Type-C power supply for power supply
- The mouse and keyboard of the USB interface, as long as the mouse and keyboard of the standard USB interface are acceptable, the mouse and keyboard can be used to control the Orange Pi development board
- USB camera
- 5V cooling fan
- 100M or 1000M network cable, used to connect the development board to the Internet
- The data cable of the Type-C interface, used to burn the image to NVMe SSD, use ADB and other functions
- OV13850 camera with 13 million MIPI interface
- Matching shell
- 3.3V USB to TTL module and DuPont line, when using the serial port debugging function, need USB to TTL module and DuPont line to connect the development board and computer
- Personal computer with Ubuntu and Windows operating systems installed
1) Ubuntu22.04 PC, Optional, used to compile Linux source code
2) Windows PC, For burning Android and Linux images
1) The website for downloading the Chinese version is:
http://www.orangepi.cn/html/hardWare/computerAndMicrocontrollers/service-and-support/Orange-pi-5.html
2) The website for downloading the English version is:
http://www.orangepi.org/html/hardWare/computerAndMicrocontrollers/service-and-support/Orange-pi-5.html
3) The information mainly includes
a. Android source code: saved on Google Drive
b. Linux source code: saved on Github
c. User manual and schematic diagram: saved on Google Drive
d. Official tools: mainly include the software that needs to be used during the use of the development board
e. Android image: saved on Google Drive
f. Ubuntu image: saved on Google Drive
g. Debian image: saved on Google Drive
Method of burning Linux image to TF card based on Windows PC
| Note that the Linux image mentioned here specifically refers to the image of the Linux distributions such as Debian or Ubuntu downloaded from the Orange Pi download page. |
How to use balenaEtcher to burn Linux image
1) First prepare a TF card with a capacity of 16GB or more. The transmission speed of the TF card must be class 10 or above. It is recommended to use a TF card of SanDisk and other brands
2) Then use the card reader to insert the TF card into the computer
3) Download the Linux operating system image file compression package that you want to burn from the Orange Pi download page, and then use the decompression software to decompress it. Among the decompressed files, the file ending with ".img" is the image file of the operating system. The size is generally more than 2GB
4) Then download the burning software of Linux image——balenaEtcher, the download address is
https://www.balena.io/etcher/
5) After entering the balenaEtcher download page, click the green download button to download the installation package of balenaEtcher. You can also select the Portable version of the balenaEtcher software through the drop-down box. The Portable version does not need to be installed, and it can be used by double-clicking to open it
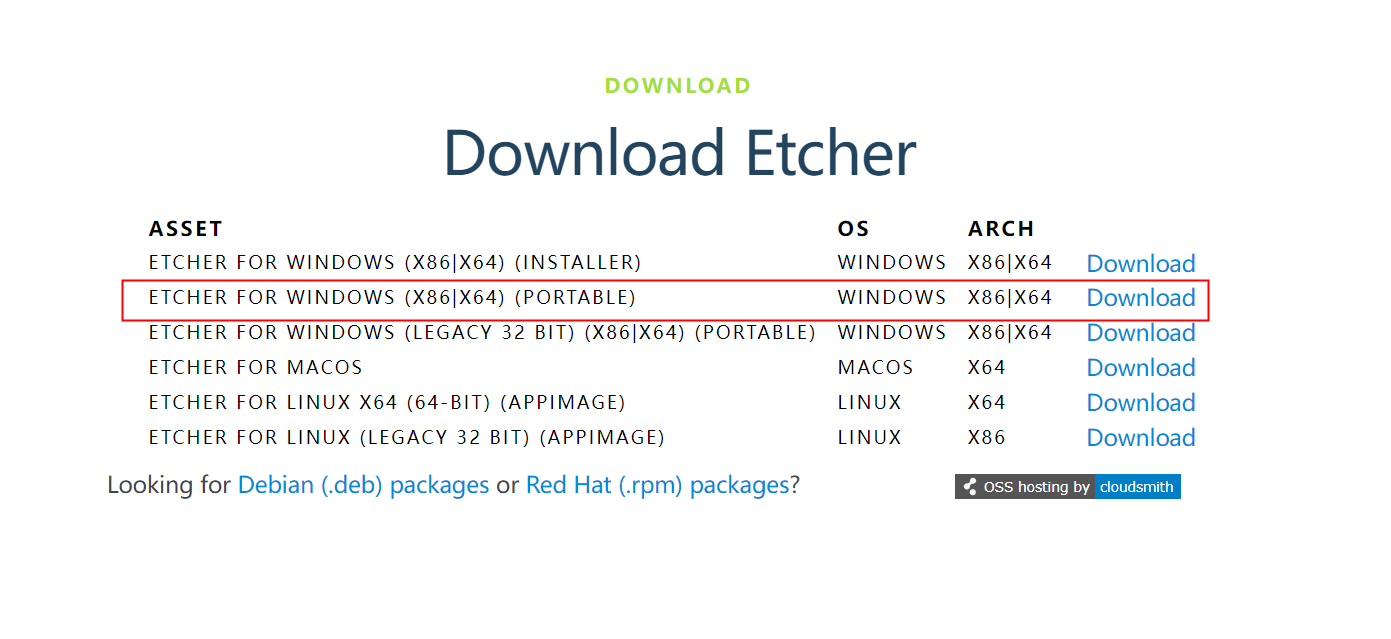
6) If the downloaded version of balenaEtcher needs to be installed, please install it before using it. If you downloaded the Portable version of balenaEtcher, just double-click to open it. The opened balenaEtcher interface is shown in the figure below
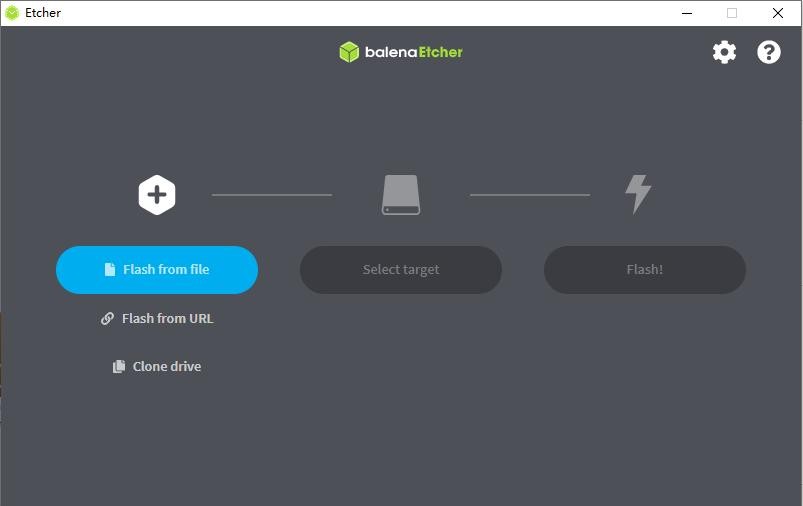
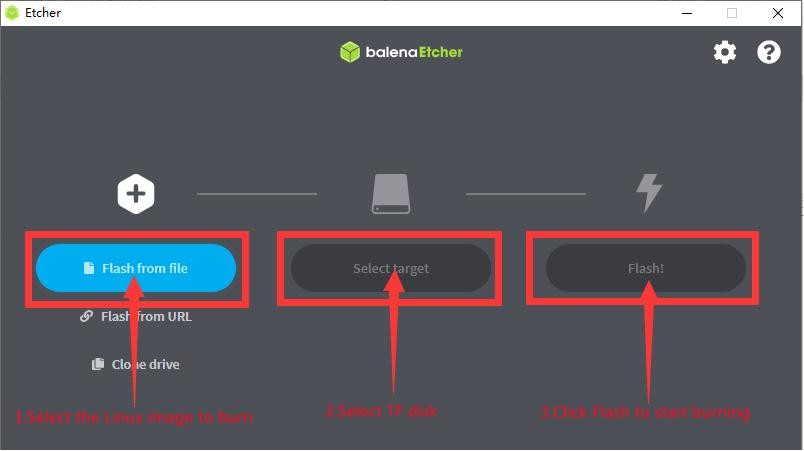
7) The specific steps to use balenaEtcher to burn the Linux image are as follows
a. First select the path of the Linux image file to be burned
b. Then select the drive letter of the TF card
c. Finally, click Flash to start burning the Linux image to the TF card
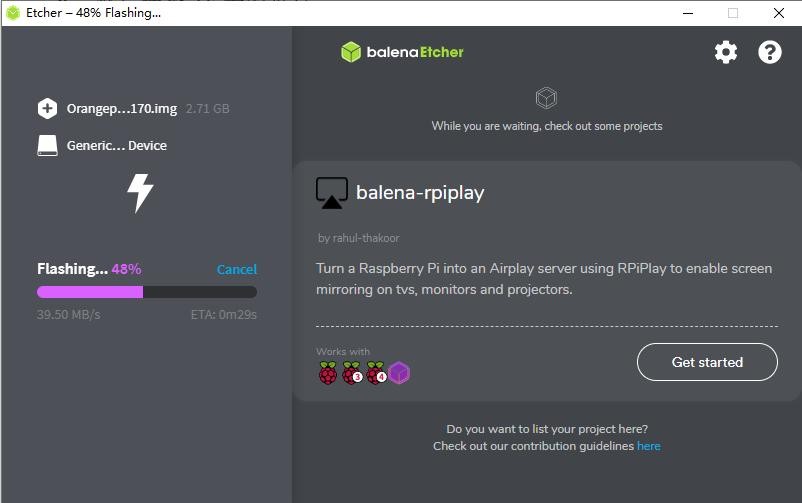
8) The interface displayed in the process of burning the Linux image by balenaEtcher is shown in the figure below, and the progress bar displays purple, indicating that the Linux image is being burned into the TF card
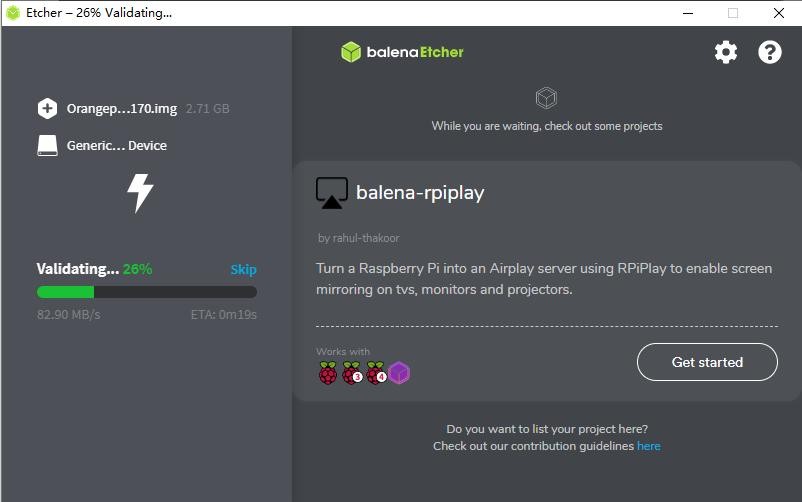
9) After burning the Linux image, balenaEtcher will also verify the image burned into the TF card by default to ensure that there is no problem in the burning process. As shown in the figure below, a green progress bar indicates that the image has been burnt, and balenaEtcher is verifying the burnt image
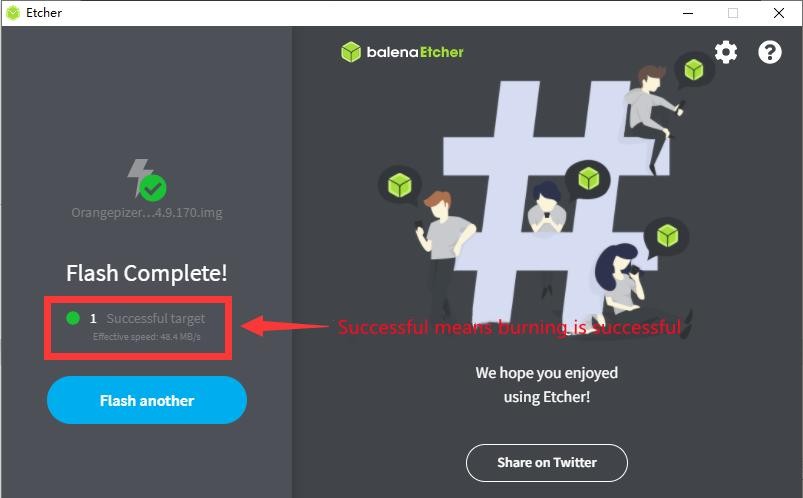
10) After successful burning, the display interface of balenaEtcher is shown in the figure below. If a green indicator icon is displayed, it means that the image burning is successful. At this time, you can exit balenaEtcher, and then pull out the TF card and insert it into the TF card slot of the development board for using
How to use Win32Diskimager to burn Linux image
How to use Win32Diskimager to burn Linux image
You can also consult the following in the Orange Pi 5 user manual:
- Method of burning Linux image to TF card based on Ubuntu PC
- How to write Linux image to SPI Flash+NVMe SSD
- How to write Linux image to SPI Flash+SATA SSD
- How to write Linux image to SPIFlash+USB storage device
How to burn Android image to TF card
1) First prepare a TF card with 8GB or larger capacity. The transmission speed of the TF card must be class10 or above. It is recommended to use a TF card of SanDisk and other brands
2) Then use the card reader to insert the TF card into the computer
3) Then download the SDDiskTool programming tool from the Orange Pi download page,please ensure that the version of the SDDiskTool tool is the latest v1.72
4) Then download the Android12 image from the Orange Pi download page
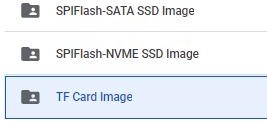
a. After opening the download link of the Android image, you can see the following three types of Android images, please select the image in the TF card image folder to download
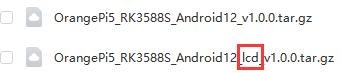
b. After entering the TF card image folder, you can see the following two images, the difference between them is:
a) The image without lcd is specially used for HDMI display and supports 8K display. If you do not use the LCD screen, please download the image without lcd
b) If you want to use LCD screen, please choose image with lcd
5) Then use the decompression software to decompress the compressed package of the downloaded Android image. Among the decompressed files, the file ending with ".img" is the Android image file, and the size is more than 1GB
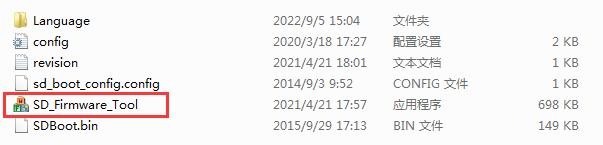
6) Then use decompression software to decompress SDDiskTool_v1.72.zip, this software does not need to be installed, just find SD_Firmware_Tool.exe in the decompressed folder and open it
7) After opening SDDiskTool, if the TF card is recognized normally, the inserted disk device will be displayed in the "Select Removable Disk Device" column. Please make sure that the displayed disk device is consistent with the drive letter of the TF card you want to burn, if there is no display, you can try to unplug the TF card
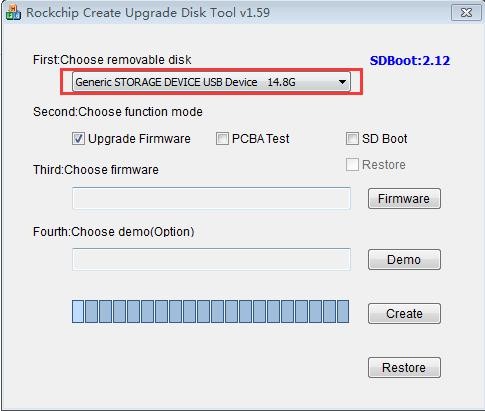
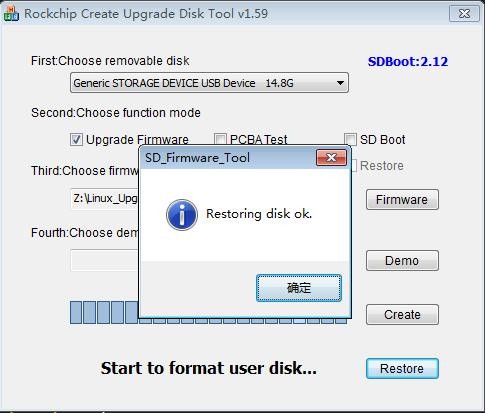
8) After confirming the drive letter, you can format the TF card first, click the Restore button in SDDiskTool, or use the SD Card Formatter mentioned above to format the TF card
9) Then start writing the Android image to the TF card
a. First check "SD Boot" in "Choose function mode"
b. Then select the path of the Android image in the "Choose firmware" column
c. Finally, click the "Create" button to start burning the Android image to the TF card
10) After burning, you can exit the SDDiskTool software, and then you can pull out the TF card from the computer and insert it into the development board to start
You can also consult the following in the Orange Pi 5 user manual:
- How to burn Android image to SPI Flash+NVMe SSD
- How to burn Android image to SPI Flash+SATA SSD
How to burn Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to TF card
1) First prepare a TF card with 8GB or larger capacity. The transmission speed of the TF card must be class10 or above. It is recommended to use a TF card of SanDisk and other brands
2) Then use the card reader to insert the TF card into the computer
3) Then download the SDDiskTool programming tool from the Orange Pi download page, please ensure that the version of the SDDiskTool tool is the latest v1.72
4) Then download the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image from the Orange Pi download page
a. After opening the download link of the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image, you can see the following two types of images, please choose the image without spi-nvme
5) Then use the decompression software to decompress the compressed package of the downloaded Orange Pi OS (Droid) image. Among the decompressed files, the file ending with ".img" is the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image file, and the size is more than 1GB
6) Then use decompression software to decompress SDDiskTool_v1.72.zip, this software does not need to be installed, just find SD_Firmware_Tool.exe in the decompressed folder and open it
7) After opening SDDiskTool, if the TF card is recognized normally, the inserted disk device will be displayed in the "Select Removable Disk Device" column. Please make sure that the displayed disk device is consistent with the drive letter of the TF card you want to burn, if there is no display, you can try to unplug the TF card

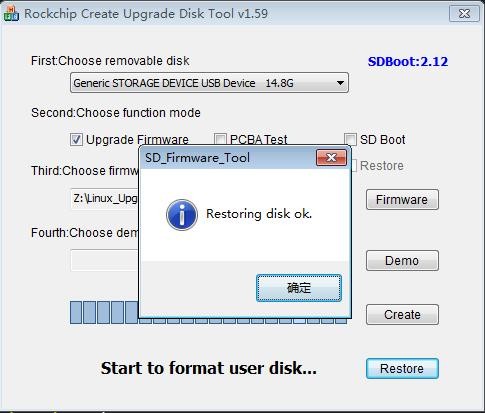
8) After confirming the drive letter, you can format the TF card first, click the Restore button in SDDiskTool, or use the SD Card Formatter mentioned above to format the TF card

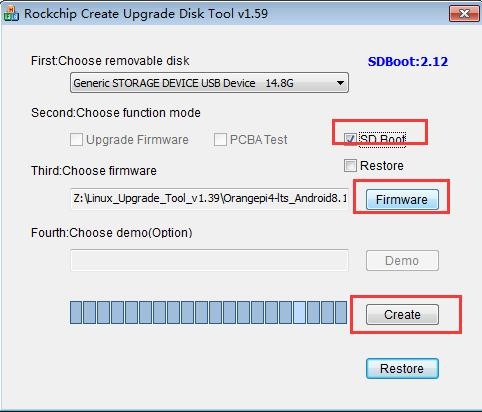
9) Then start to write the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to the TF card
a. First check "SD Boot" in "Choose function mode"
b. Then select the path of the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image in the "Choose firmware" column
c. Finally, click the "Create" button to start burning the Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to the TF card

10) After burning, you can exit the SDDiskTool software, and then you can pull out the TF card from the computer and insert it into the development board to start

You can also consult the following in the Orange Pi 5 user manual:
- Burn Orange Pi OS (Droid) image to SPIFlash + NVMe SDD
Start Orange Pi 5
1) Insert the TF card with the burned image into the TF card slot of the Orange Pi development board. If the image of SPIFlash+NVMe SSD has been burnt, then there is no need to insert a TF card, just make sure that the NVMe SSD is inserted into the development board normally.
2) The development board has an HDMI interface, and the development board can be connected to a TV or HDMI display through an HDMI-to-HDMI cable. If you buy an LCD screen, you can also use the LCD screen to display the system interface of the development board. If there is a Type-C to HDMI cable, the system interface of the development board can also be displayed through the Type-C interface.
3) Connect a USB mouse and keyboard to control the Orange Pi development board.
4) The development board has an Ethernet port, which can be plugged into a network cable for Internet access.
5) Connect a high-quality power adapter with a 5V/4A USB Type-C interface.

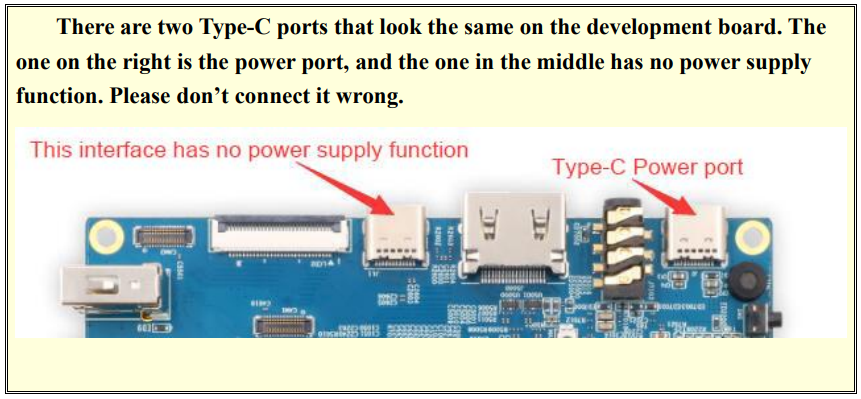
6) Then turn on the switch of the power adapter. If everything is normal, you can see the startup screen of the system on the HDMI monitor or LCD screen.
7) If you want to view the output information of the system through the debugging serial port, please use the serial cable to connect the development board to the computer. For the connection method of the serial port, please refer to the section on how to use the debugging serial port in the Orange Pi 5 user manual:
Linux system instructions
Ubuntu images and Debian images are generally referred to as Linux images (they both use the Linux kernel), so when you see a Linux image or Linux system in the manual, it refers to a image or system like Ubuntu or Debian.
Many people will have doubts about whether they can use pure Ubuntu or pure Debian systems (pure here can be understood as systems downloaded from Ubuntu or Debian official websites). The answer is no, because Ubuntu and Debian do not provide an adapted system for the Orange Pi development board.
We can see from the official websites of Ubuntu and Debian that they both support the arm64 architecture (the SOC of the development board is the arm64 architecture), but please note that the support mentioned here refers only to the arm64 version of the software warehouse provided by Ubuntu or Debian (including Tens of thousands of software packages) or rootfs (these are the packages that Orange Pi uses when making Ubuntu or Debian systems). To make an Ubuntu or Debian system that can be used for a certain development board also needs to transplant U-boot and Linux kernel, etc., as well as repair the encountered bugs and optimize some functions, all of which are done by Orange Pi.
If Linux distributions such as CentOS, Kali, or OpenWRT are not ported by other developers or ported and adapted by themselves, they cannot be used on the development board of Orange Pi (hardware running these systems is no problem).
In addition, people often ask whether the system of other development boards can be used on the Orange Pi development board. The answer is no, because the chips and circuit connections used by different development boards are generally different. A system developed for a certain development board basically cannot be used on other development boards.
1) Supported Linux image types and kernel versions
2) Onboard LED Light Test Instructions
3) Network connection test
Check Ethernet port test
Check WIFI connection test
Check How to set a static IP address
Check How to use AP6275P PCIe network card
Check AP6275P PCIe NIC creates WIFI hotspot via create_ap
4) HDMI test
Check HDMI display test
Check HDMI to VGA display test
Check HDMI resolution setting method
5) How to use Bluetooth
6) USB interface test
Check Connect USB mouse or keyboard to test
Check Connect USB storage device test
Check USB wireless network card test
Check USB camera test
7) Audio Test
Check Testing audio methods on desktop systems
Check The method of using commands to play audio
Check Method of using commands to test recording
8) 26 Pin Interface Pin Description
For more detailed information on Linux system instructions, you can check the Orange Pi 5 user manual.
Instructions for the use of the Android 12 system
1) How to use the wireless network card
2) 26Pin interface GPIO, UART, SPI and PWM test
Check 26pin GPIO port test
Check 26pin UART test
Check 26pin's PWM test
Check 26pin's SPI test
You can also consult the following in the Orange Pi 5 user manual:
- Linux SDK——orangepi-build instructions for use
- The compilation method of the Android 12 source code
Parameter table
- Wide range of application scenarios
It can be widely applied to tablets, edge computing, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, AR/VR, intelligent security, smart home and other fields, covering AIoT various industries.
| CPU |
Rockchip RK3399 (28nm HKMG process) |
| SoC | Rockchip RK3588S (8nm LP process) |
| CPU |
|
| GPU |
|
| NPU | Built-in AI accelerator NPU with up to 6 TOPS, supports INT4/INT8/INT16 mixed operation |
| PMU | RK806-1 |
| RAM | 4GB/8GB/16GB /32GB(LPDDR4/4x) |
| Memory |
|
| USB |
|
| Video Output |
|
| Camera |
|
| Audio |
|
| Ethernet | 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet |
| Expansion Port | For extending UART, PWM, I2C, SPI, CAN and GPIO interfaces. |
| M.2 M-KEY Socket Expansion Slot |
|
| Button |
|
| Power Source | Support Type-C power supply, 5V @ 4A |
| LED |
|
| Debugging | 3 Pin debug serial port (UART) |
| Supported OS | Orangepi OS(Droid)、Orangepi OS(Arch)、Ubuntu、Debian、Android12 |
| Dimensions | 62mm*100mm |
| Weight | 46g |